What’s new in our Optical Modeling and Design Software?
Spectral and Angular Sensitivity of Special Gratings
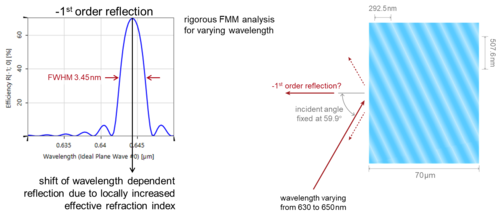
Special grating designs enable the engineering of their properties. For example, holographic volume gratings and resonant waveguide gratings are well known for their sensitivity with respect to wavelength and incidence angle. Due to such properties, they are often applied in optical metrology. We analyze these two types of gratings in VirtualLab Fusion, particularly, by checking their spectral and angular sensitivity.
Read moreDemonstrating a Flash LiDAR
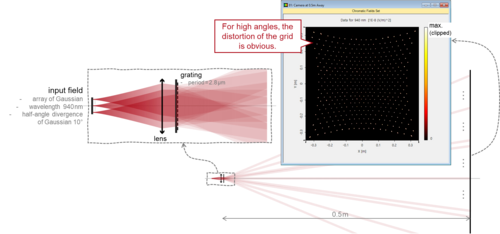
In recent years, LiDAR (light detecting and ranging) technology has started to play a role in consumer optics products. Particularly, the flash LiDAR solution – in a solid-state design – fits well to the design of modern smart devices, like the iPhone 12 from Apple, and their iPad Pro products. Such optical devices often consist of both lenses and diffractive optics elements. We build a flash LiDAR system with an array of source via the programmable Parameter Run in VirtualLab Fusion, and we analyze its working principle in both the spatial and the spatial frequency domains.
Read moreOAM Measurement with Freeform Optical Elements
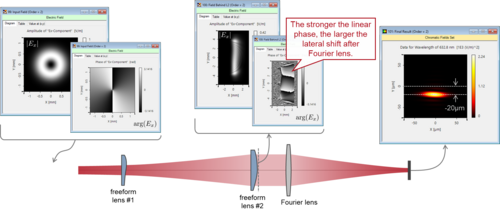
Capacity for ever larger amounts of information is consistently sought after for optical communications and data transfer. One approach is to employ optical beams with orbital angular momentum (OAM), which can be generated, for instance, with spiral phase plates. Counterpart to its generation, the measurement of OAM, i.e., the decoding of the information, is of equal importance. Following the concept of M. P. J. Lavery et al., we demonstrate how to measure OAM with the help of two customized freeform optical elements in VirtualLab Fusion.
Read moreGenerating Orbital Angular Momentum (OAM) Beams
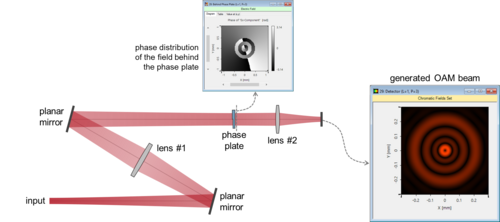
Optical beams with orbital angular momentum (OAM) have proved useful for different applications, from quantum optics to optical telecommunication and to microscopy. Different methods have been proposed for the generation of such beams and here we demonstrate, in VirtualLab Fusion, how to use a spiral phase plate to generate beams carrying OAM. A programmable interface is used to describe the spiral phase plate with customizable parameters, and the microstructure component is used for its modeling.
Read moreSave your seat for our Webinar on Gratings!
In order to adapt to different time zones worldwide, we will hold this webinar twice (all times CEST):
22 October | 10:00 – 11:00 & 18:00 – 19:00
Read moreAnalyzing CMOS Sensor with Microlens on Top
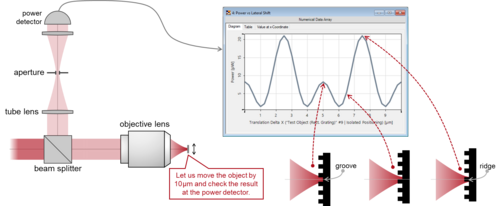
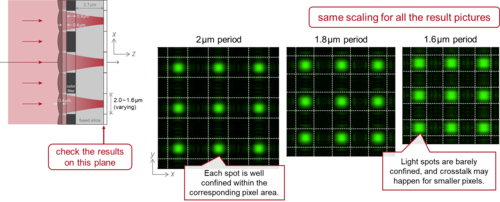
By continuously decreasing the pixel size of CMOS sensors, better and better spatial resolution has been achieved in recent decades, with the tendency expected to continue. This, however, turns the spotlight onto the microlenses sitting on top of each pixel. Can a microlens still focus light as expected when the pixel size edges closer to the wavelength? We investigate this issue with VirtualLab Fusion at selected examples.
Read moreResolution Investigation
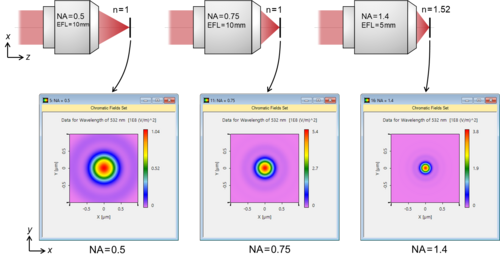
How to resolve better is an ever-present question in optical science, and how to judge the resolution of an optical system is therefore an important question. Following Ernst Karl Abbe (1840-1905) and John William Strutt, 3rd Baron Rayleigh (1842-1919), we demonstrate Abbe’s resolution limit and the Rayleigh criterion in VirtualLab Fusion and show how to use both analyses to evaluate the performance of typical imaging systems.
Read moreGeneration of Arbitrary Vector Beams with Interferometric Setup
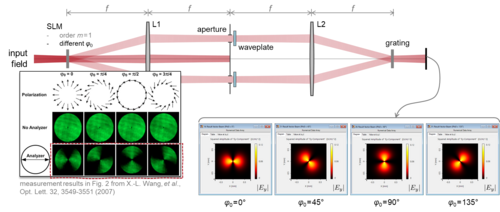
Cylindrical vector beams have been found to be helpful in various applications. Following the work of X.-L. Wang et al., we build up an interferometric setup for the generation of vector beams. The setup consists of various types of optical components, including SLMs, gratings, apertures, waveplates and lenses. With the programmable function, the SLM transmission can be arbitrarily defined and varied, as in the example below. We demonstrate the generation of vector beams in VirtualLab Fusion and compare the results against those from the literature.
Read more