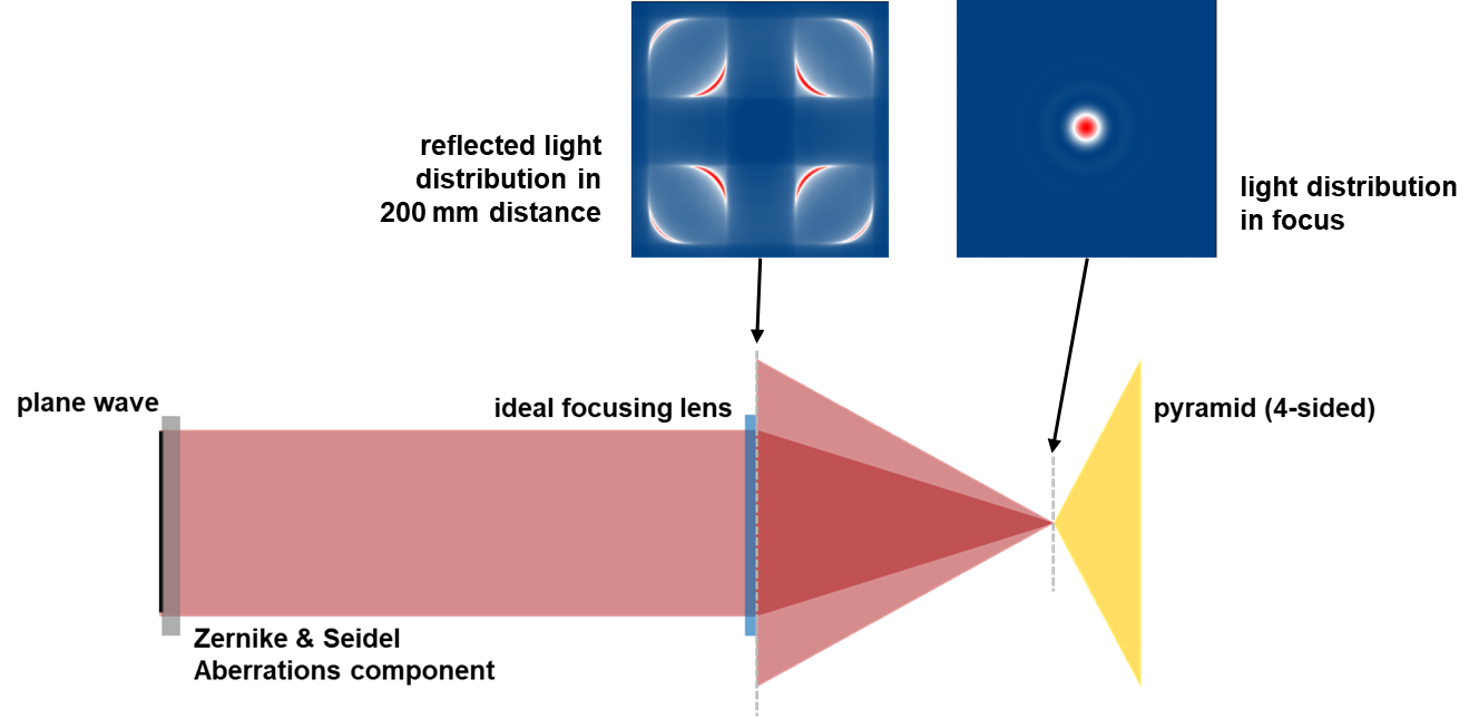
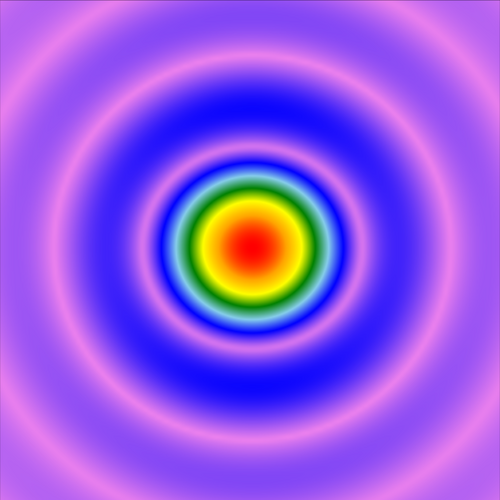
Simulation of Reflective Pyramid Wavefront Sensor
Abstract
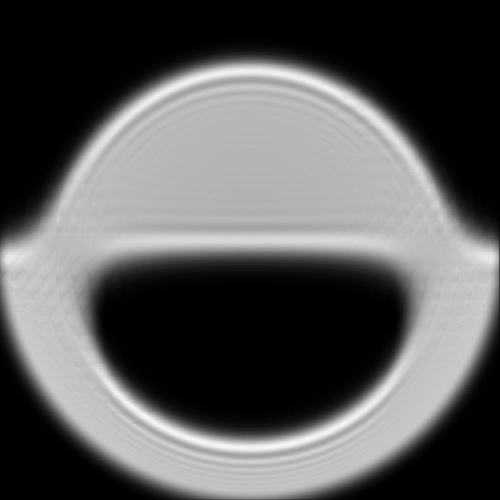
Wavefront sensors that use a pyramid shaped prism or reflector (PyWFS, for pyramid wavefront sensor) are known for their high contrast and better wavefront sensitivity compared to conventional Shack-Hartmann sensors, e.g., for the search for extrasolar planets in astronomy. Hence, this type of wavefront sensors are used in special telescopes (e.g., at Keck Observatory), usually in the infrared (IR) spectral range. A PyWFS typically consists of a four-sided prism, re-imaging optics, and an appropriate detector. In this example, we show the modeling of the characteristic light pattern of such a pyramid-shaped prism for different types of aberrations, by applying VirtualLab Fusion’s fast physical optics Field Tracing technology.
VirtualLab Fusion Configuration
-
 VirtualLab Fusion
VirtualLab Fusion