Analysis and Design of Highly Efficient Polarization Independent Transmission Gratings
Abstract
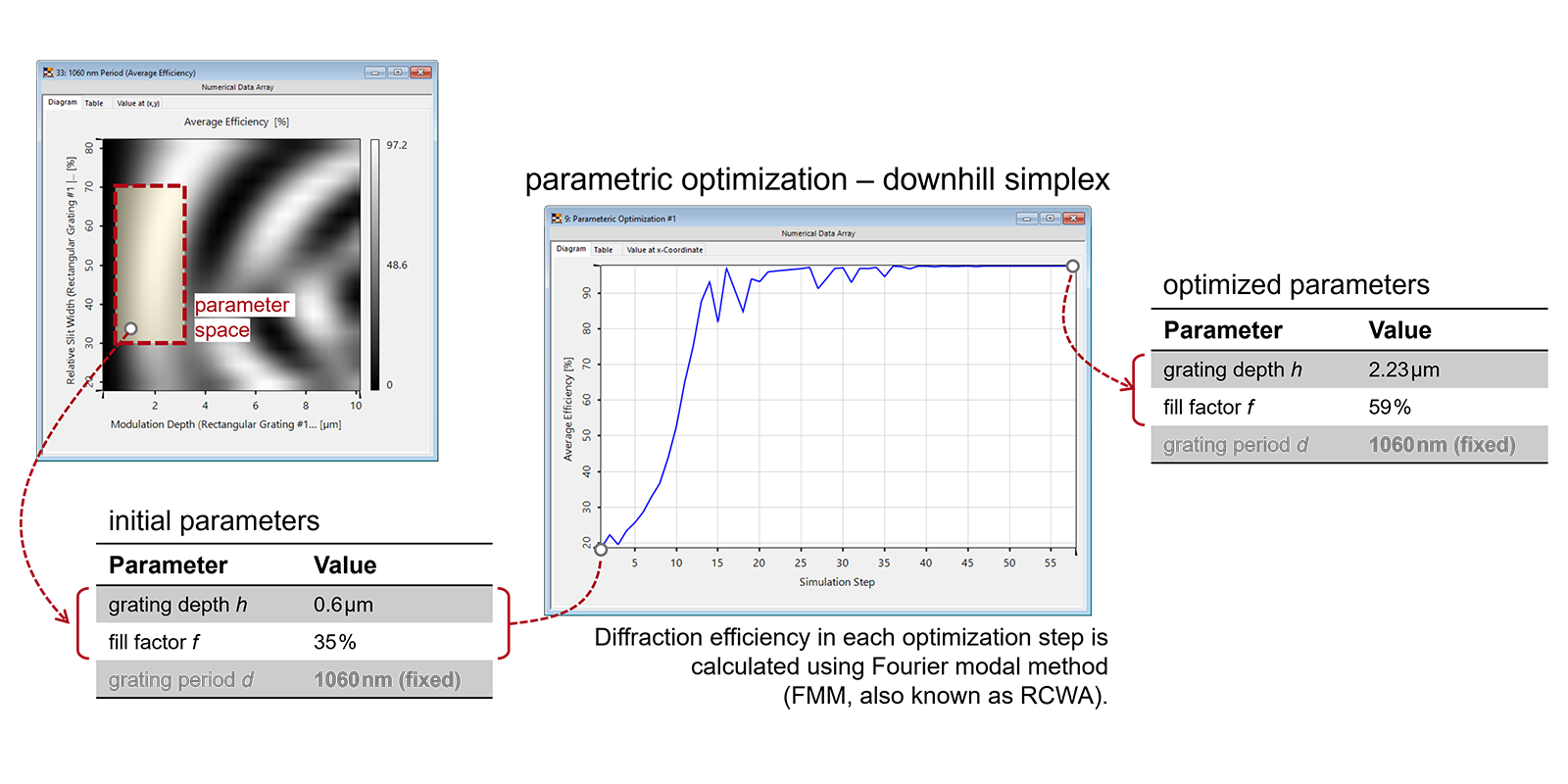
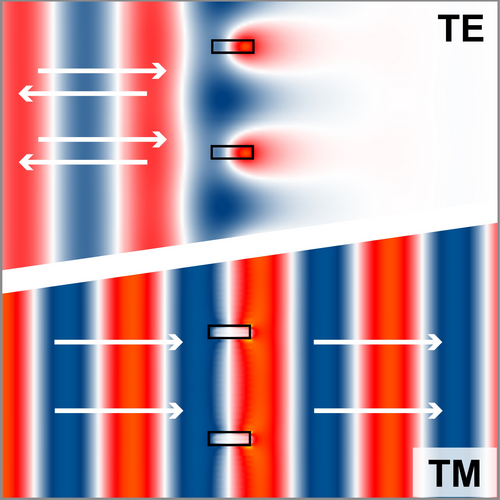
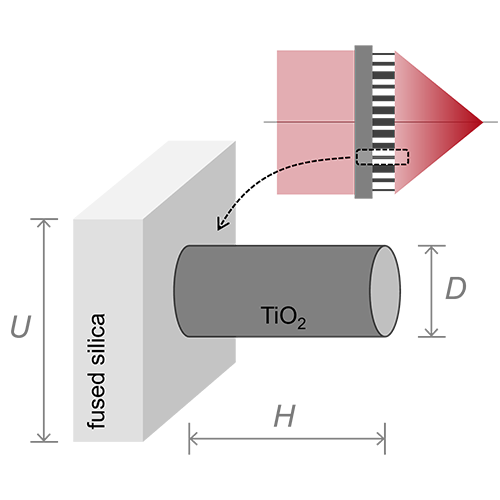
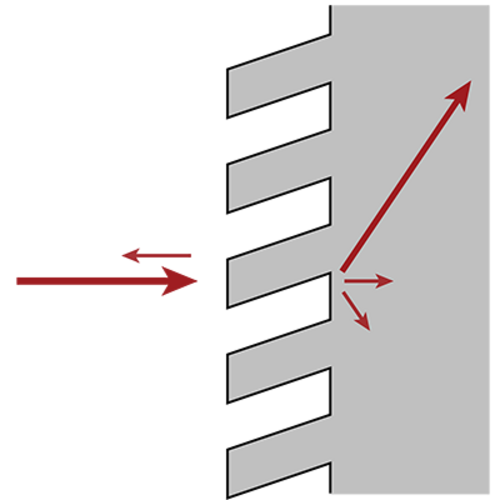
Gratings, especially those with feature size comparable to the wavelength, are known to possess polarization-dependent optical properties. That makes it difficult to design gratings with high diffraction efficiencies for arbitrary polarizations. Following the concept reported in literature [T. Clausnitzer, et al., Proc. SPIE 5252, 174-182 (2003)], we show how to analyze the polarization-dependent property of gratings rigorously, as well as how to use parametric optimization to design polarization-independent gratings with high diffraction efficiency.
VirtualLab Fusion Configuration
-
 VirtualLab Fusion
VirtualLab Fusion
-
 Grating Package
Grating Package