Configuration of the FMM/RCWA
Definition
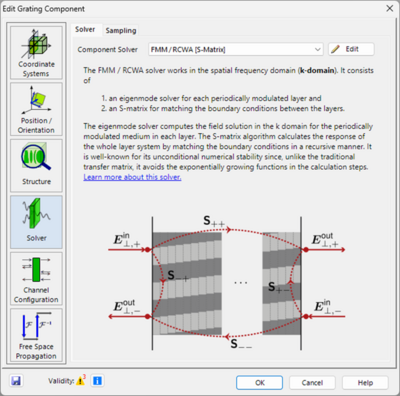
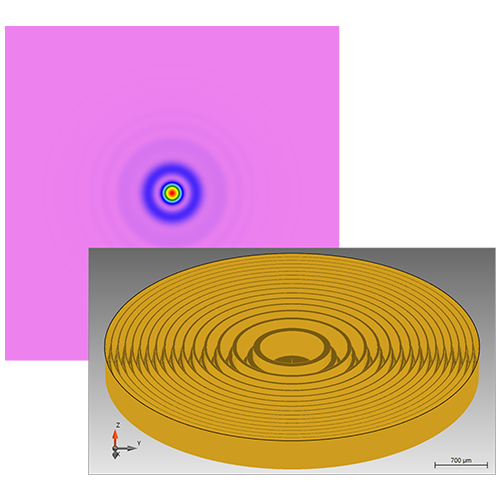
The Fourier Modal Method/Rigorous Coupled Wave Analysis (FMM/RCWA) solver is an eigenmode solver in the spatial frequency domain (k domain) used among others in the Grating component. While theoretically rigorous, in praxis the solver’s accuracy depends on the number of diffraction orders taken into account, which is accessible via the Edit button.
Usage Recommendation
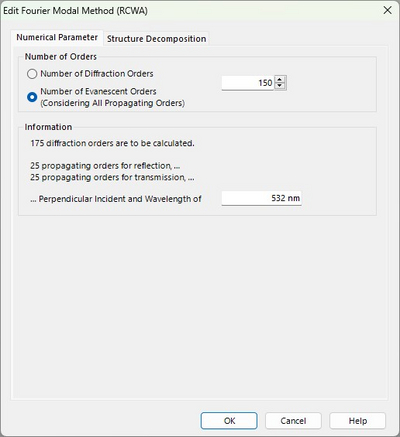
In the Numerical Parameters tab, users can define the number of orders considered by the FMM/RCWA solver, either by specifying the diffraction orders directly or by setting the number of evanescent orders to include. We recommend the latter option as it automatically accounts for all propagating orders plus the specified evanescent orders.
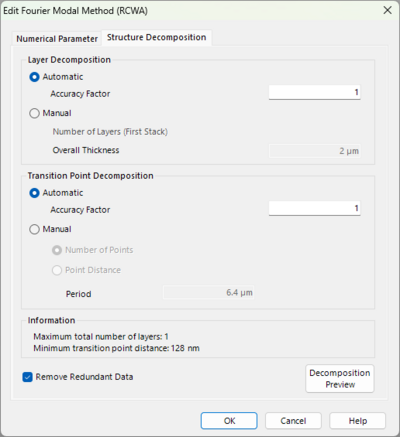
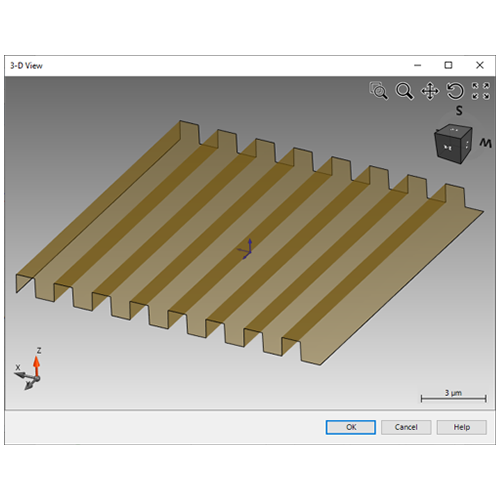
The solver always functions on a discretized structure. Hence, the Structure Decomposition tab controls the sampling parameters of the discretization using Transition Points (X, Y) and Layers (Z). A preview is available to visualize the current discretization.
For structures consisting out of dielectric materials the automatic settings typically are sufficient. For certain scenarios however, such as metal surfaces that require more evanescent orders or meta-structure which are notorious for their small feature sizes, manual adjustments may be necessary. We suggest always testing the convergence of the FMM/RCWA solver by first fixing the number of orders and refining the discretization. Once stable results are achieved, increase the number of orders (e.g., via a Parameter Run) until convergence is reached.