Working Principle of Optical Coherence Tomography
Abstract
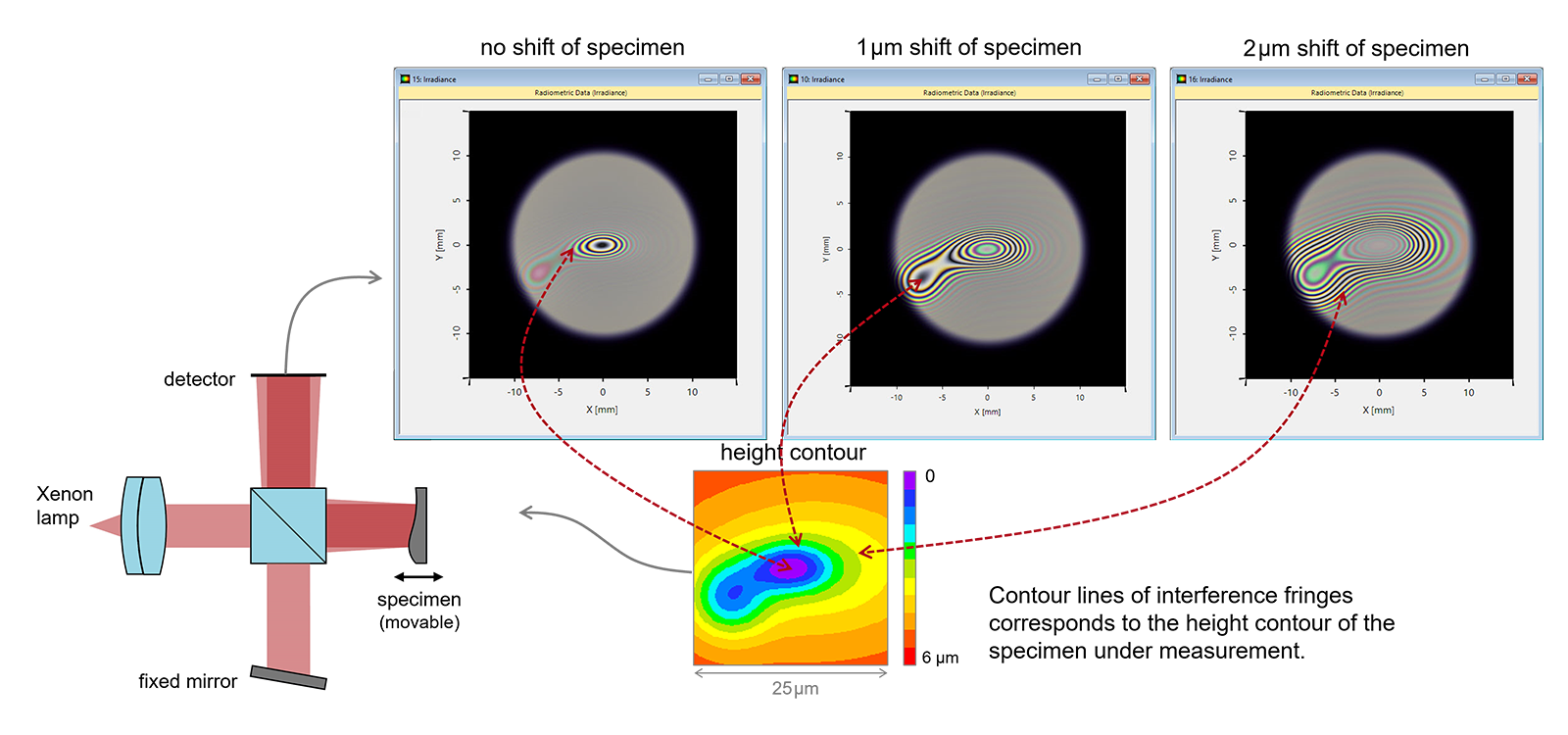
VirtualLab Fusion’s various interoperable modeling techniques and non-sequential simulation engine facilitate an efficient modeling of interferometer tasks, such as optical coherence tomography. In this example a Michelson interferometer with a Xenon lamp is constructed and used to measure a specimen with a smoothly modulated surface.
VirtualLab Fusion Configuration
-
 VirtualLab Fusion
VirtualLab Fusion