Modeling of a Herriott-Cell
Abstract
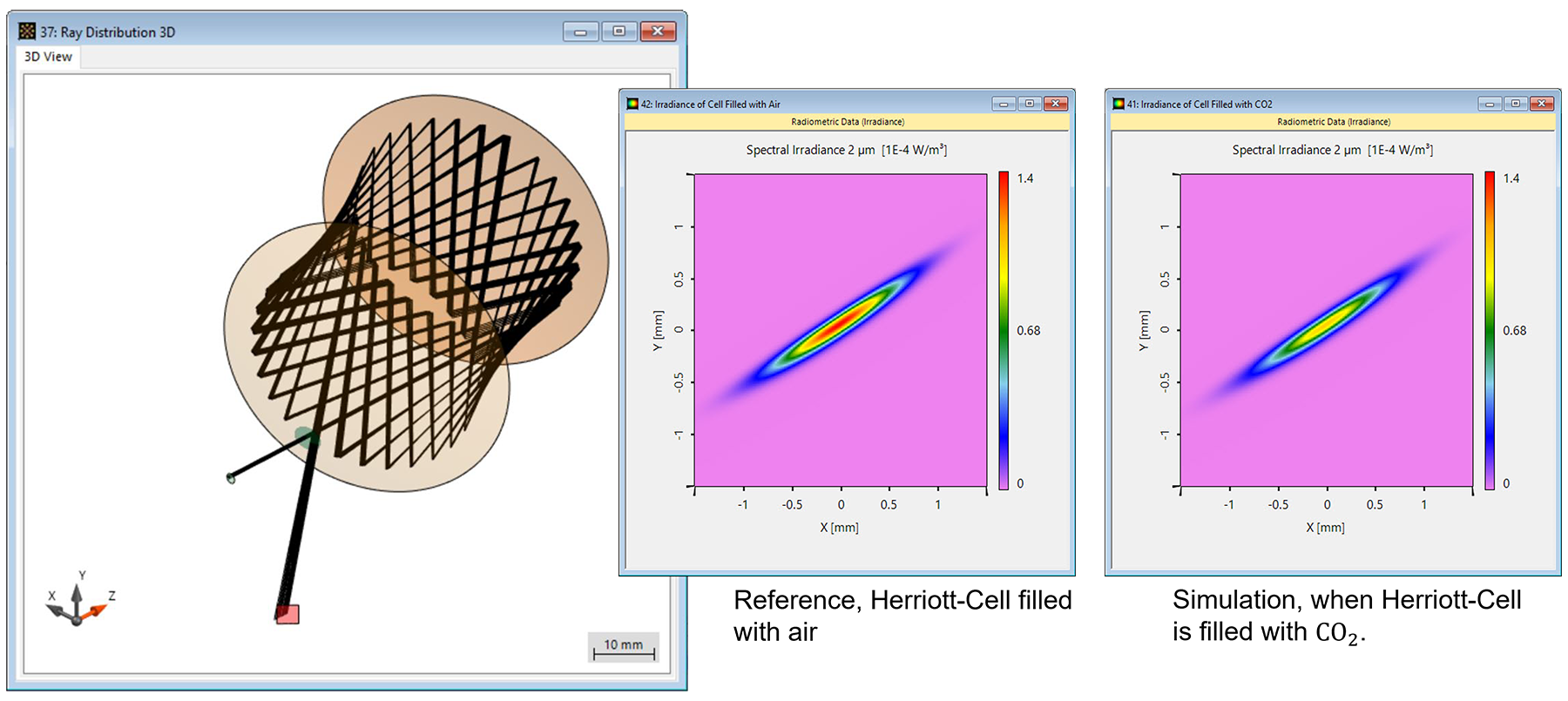
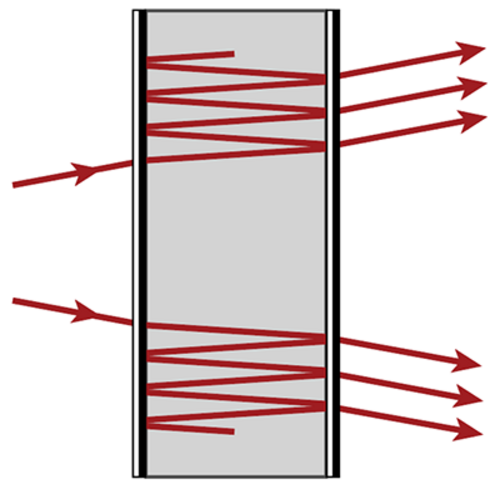
In spectroscopy of gases, in order to obtain a sensitive enough measurement of the absorption, it is often required to have long optical path lengths. Multiple-pass cells, where the gas-filled volume is encased between mirrors, are a way of fulfilling this requirement while at the same time controlling beam divergence on the way and preempting the need for extremely large devices. The Herriott cell is one example of this kind of system, characterized by the use of two spherical mirrors with a single off-axis hole drilled into one of them to allow for the entry and exit of the beam. The curvature of the mirrors redirects the beam and controls its divergence. In this use case, we investigate the simulation of a Herriott cell with the optics modeling and design software VirtualLab Fusion.
VirtualLab Fusion Configuration
-
 VirtualLab Fusion
VirtualLab Fusion
-
 Grating Package
Grating Package