Frustrated Total Internal Reflection (FTIR) in a Cube Beam Splitter
Abstract
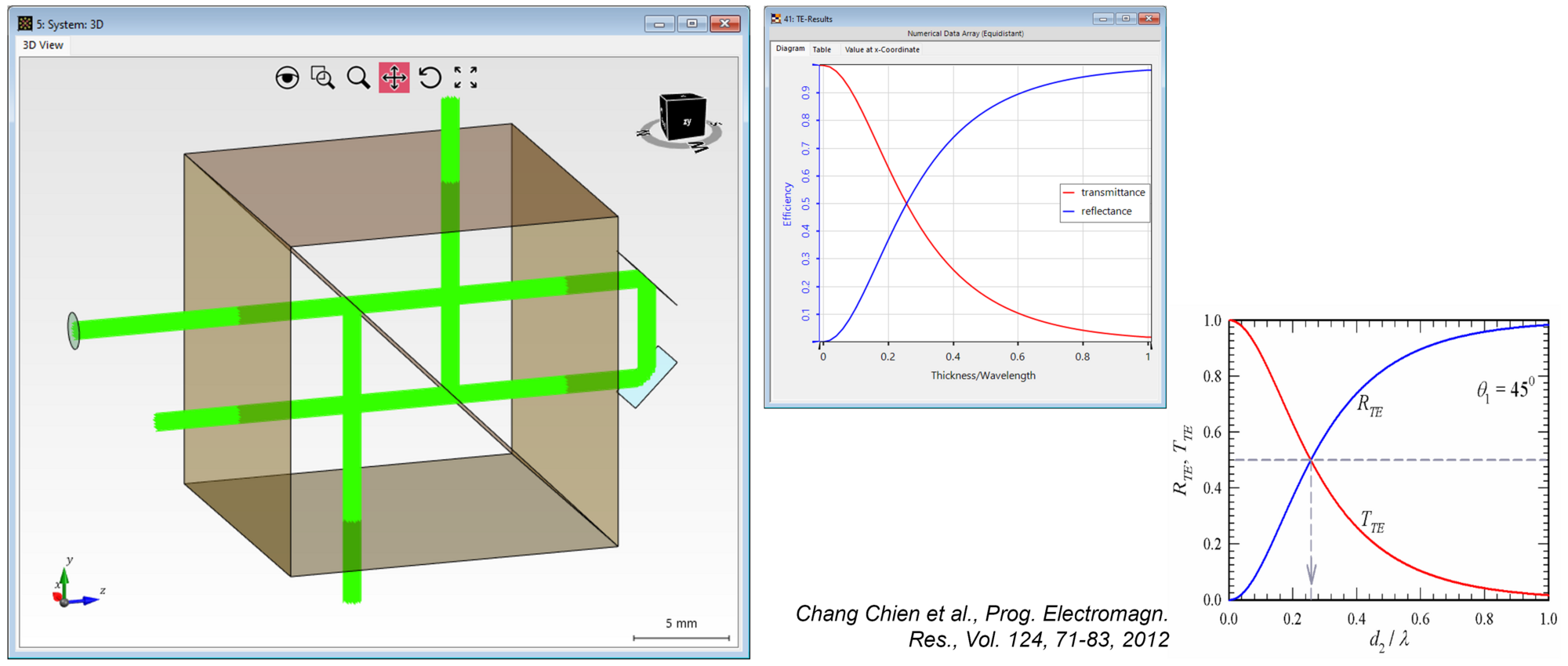
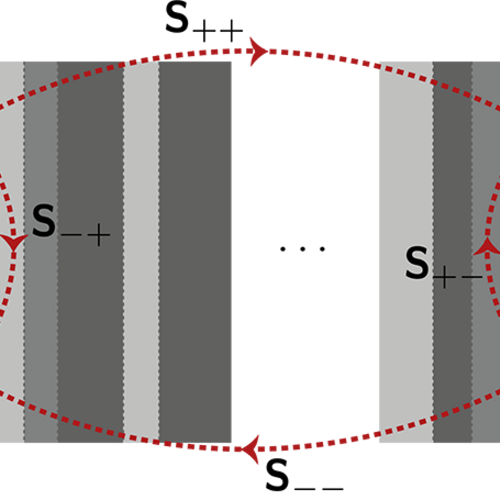
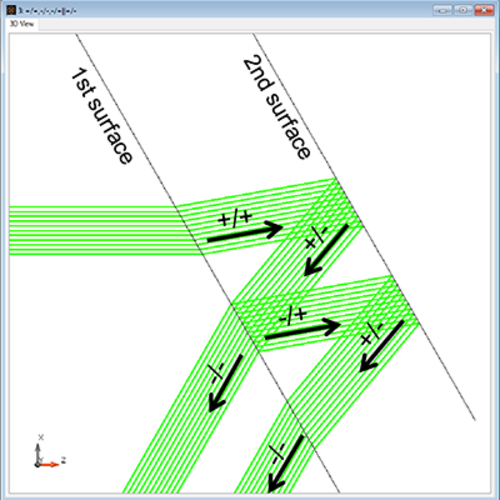
Optical beam splitter devices play a crucial part in many applications in the areas of spectrometry, interferometry and optical communication. A common type of beam splitter is based on the phenomenon of Frustrated Total Internal Reflection (FTIR): a first glass prism is set up so that the incident light impinges on one of its surfaces under conditions of total internal reflection, with a second prism placed directly behind it, so that only a very thin layer of a less dense material (air, for instance) separates the two prisms. If the separation layer is thin enough, the total internal reflection will be at least partially frustrated by the evanescent waves tunneling through the spacing, thus achieving a redistribution of the incident energy between the two outputs of the splitter which can be adjusted through the spacing.
VirtualLab Fusion Configuration
-
 VirtualLab Fusion
VirtualLab Fusion