High-NA Beam Splitter Optimization with User-Defined Merit Functions
Abstract
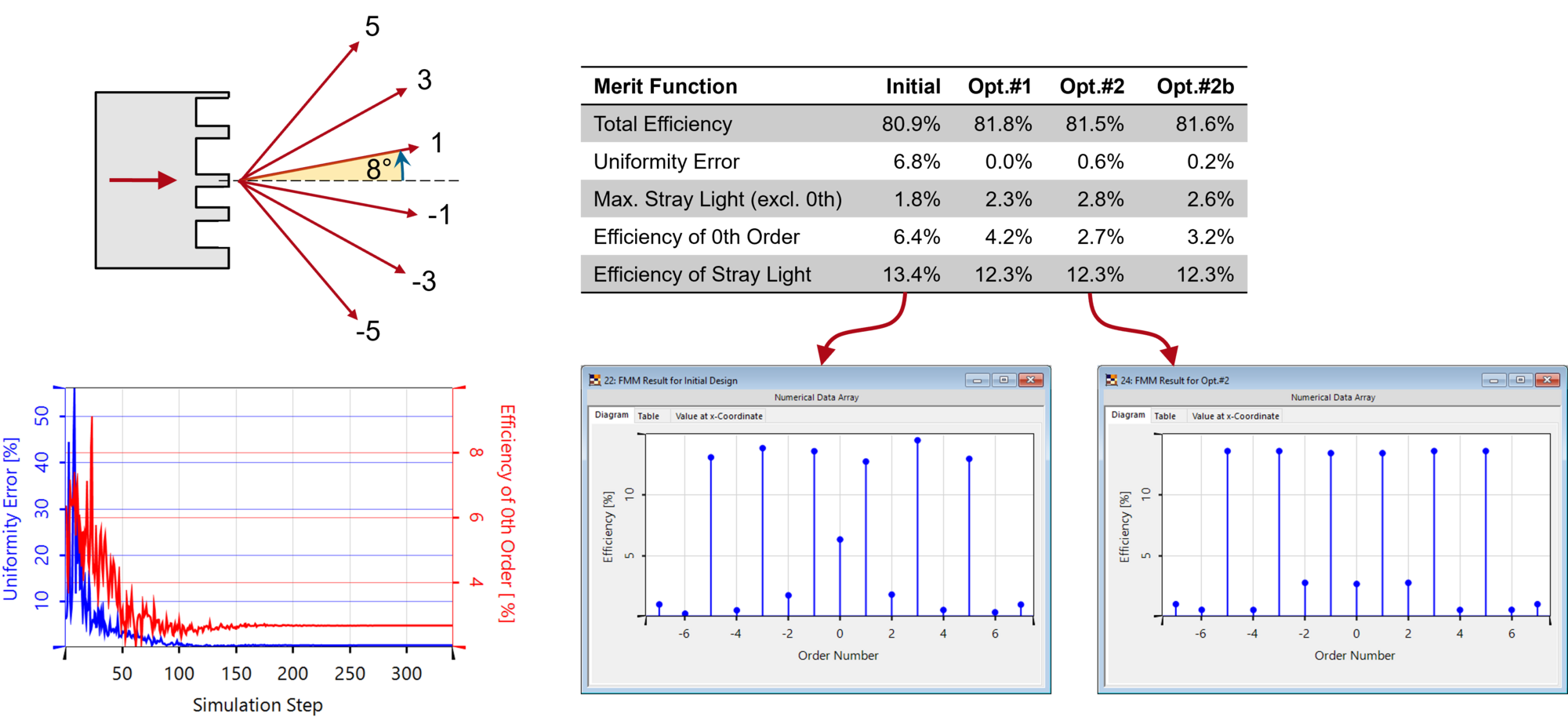
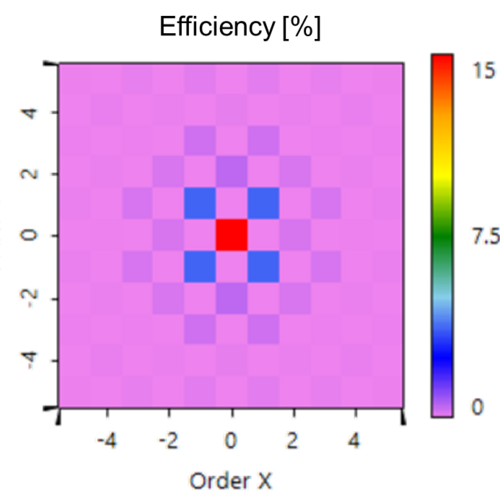
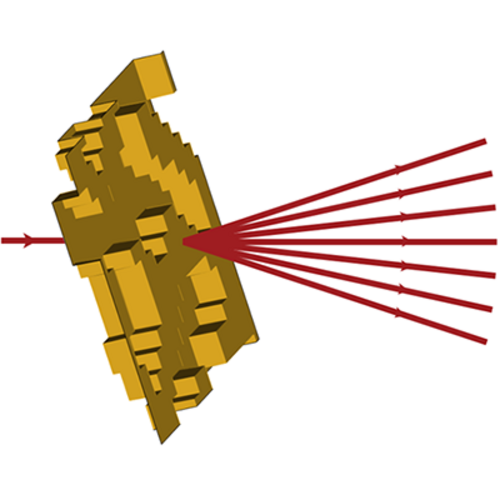
Diffractive beam splitters are often designed by applying certain paraxial approximations due to the direct relation between phase and structure and vice versa, which these algorithms provide. In case of non-paraxial or even high-NA splitters these approximations will introduce some inaccuracy and hence at least a rigorous analysis is advised, if not an additional rigorous post-optimization. In this use case, such rigorous evaluations are performed for an exemplary binary 1:6 splitter, using the odd diffraction orders. For this purpose, the structure of the initial system is parametrized, and a set of user-defined merit functions are defined via the Programmable Grating Analyzer. For the parametric optimization and subsequent tolerance analysis, the rigorous Fourier Modal Method (FMM) is used.
VirtualLab Fusion Configuration
-
 VirtualLab Fusion
VirtualLab Fusion
-
 Grating Package
Grating Package