Thin Element Approximation (TEA) vs. Fourier Modal Method (FMM) for Grating Modeling
Abstract
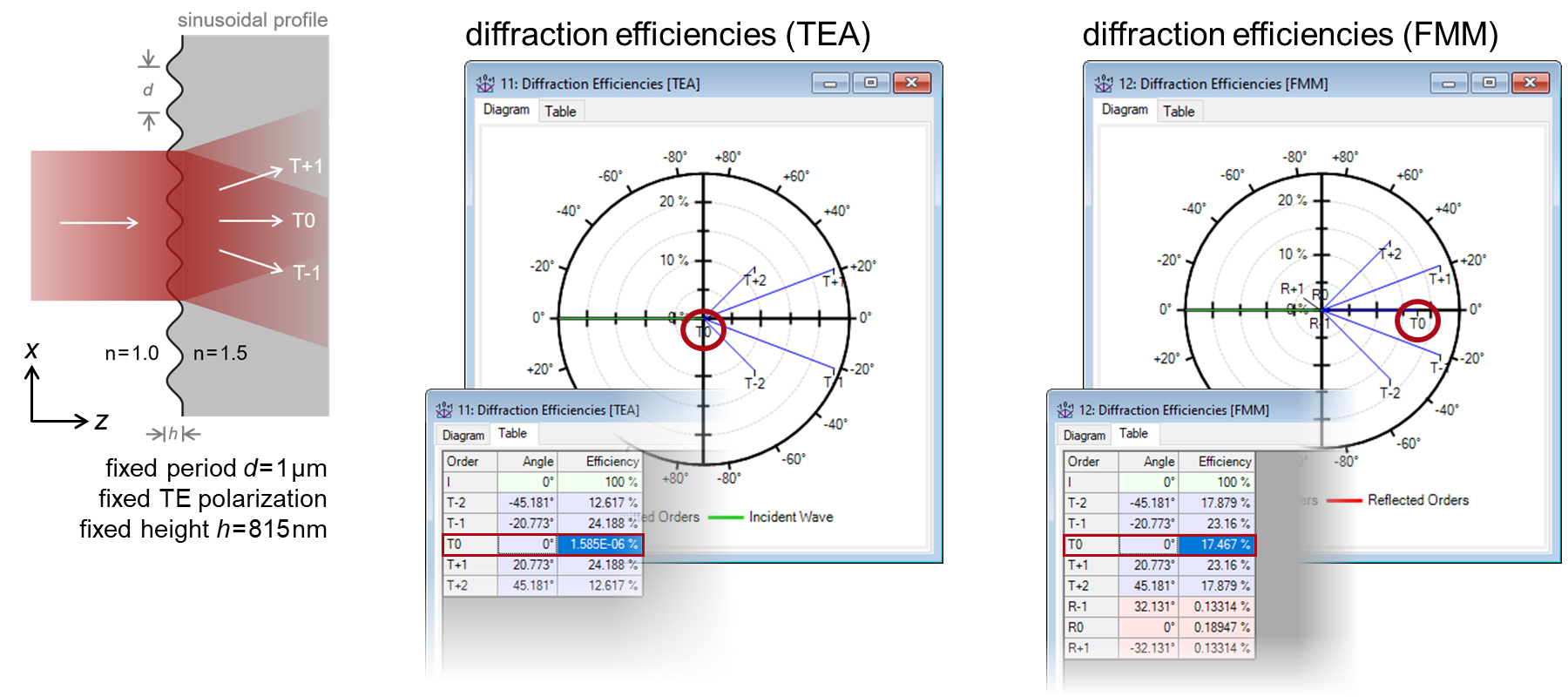
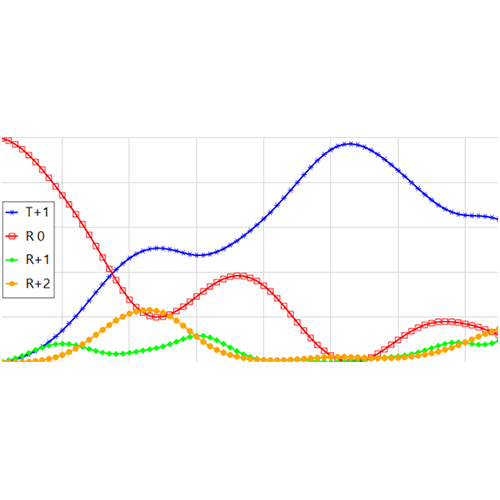
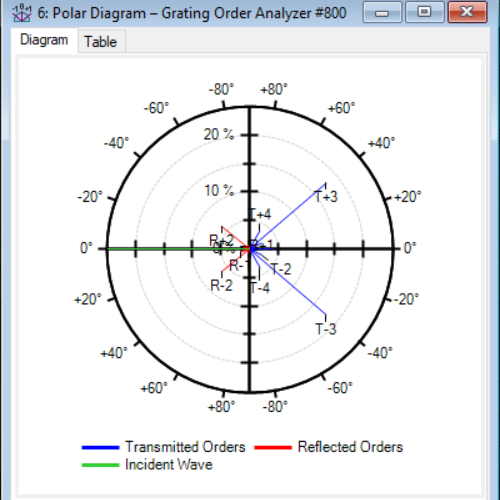
The Thin Element Approximation (TEA) is a widely-used method in Fourier optics to calculate the diffraction efficiency of gratings. However, it is also known that the approximation becomes inaccurate for smaller grating periods, means closer to the wavelength of light. In this example, two types of transmission gratings are selected to showcase this effect: sinusoidal and blazed. We use both TEA and FMM (also known as RWCA, which is rigorous) to analyze such gratings with varying period, and by comparing the results, we investigate the behavior of the two methods.
VirtualLab Fusion Configuration
-
 VirtualLab Fusion
VirtualLab Fusion
-
 Grating Package
Grating Package